Ileana Arsenescu
Article received on the 13th August 2012. Article accepted on the 27th August 2012.
„Prof. Dr. C. C. Iliescu“ Emergency Institute for Cardiovascular Diseases, Bucharest
Dr. Ileana Arsenescu, „Prof. Dr. C. C. Iliescu” Emergency Institute for Cardiovascular Diseases, Bucharest
Pseudoaneurysms represent one of the relatively frequent complications of interventional procedures, especially after therapeutic maneuvers.
The clinical diagnosis is based on the development of a pulsating formation at the puncture site, presenting a continuous murmur.
Ultrasonographic diagnosis:
– pseudoaneurysm appears as a well defined cavity whose content is initially anechogenic (Figure 1). The shape and dimensions vary from one case to another, with the possibility of multiple simultaneous pseudoaneurysms. The initial color Doppler examination shows the red-blue filling phase, typical for aneurysms (Figure 2). The spectral Doppler correspondent for this aspect is the low speed dual phase signal (Figure 3). Most false aneurysms evolve towards thrombosis, developing echogenic, nonhomogeneous content and loss of its Doppler signal.
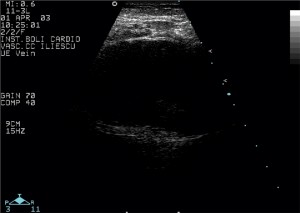
Figure 1. Post-coronarography inguinal pseudoaneurysm. The aspect is of a well-defined formation, with the predominance of anechogenic content. Discreet spontaneous contrast near the posterior wall.
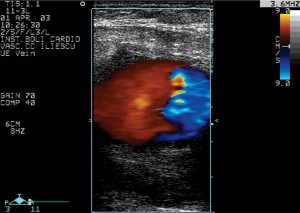
Figure 2. The Doppler color examination shows the bicolor filling, with a clear delimitation between the red and the blue zone.
Figure 3. The Doppler signal in the aneurysm is dual phase, with low speeds.
– The communication with the artery usually has a sinuous trajectory, where a dual phase systolic signal is registered. During the systole the blood flows from the high pressure artery towards the low pressure pseudoaneurysm. During the diastole the pressure is higher in the pseudoaneurysm, which leads to a large back-flow to the artery (Figure 4 and 5).
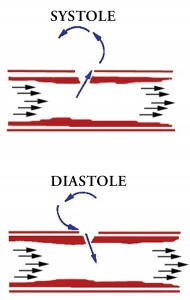
Figure 4. Diagram showing the mechanism generating the Doppler signal from the pseudoaneurysm supply path.
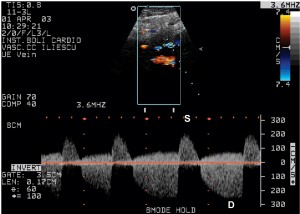
Figure 5. The Doppler signal in the communication between the femoral artery and the aneurysm (S = systole, D = diastole).
– The Doppler signal is usually normal in the artery supplying the blood for the pseudoaneurysm.
 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a